 New to building your own computer or looking to refresh past knowledge about video cards ? This is the right article for you !
New to building your own computer or looking to refresh past knowledge about video cards ? This is the right article for you !
1. The Interface
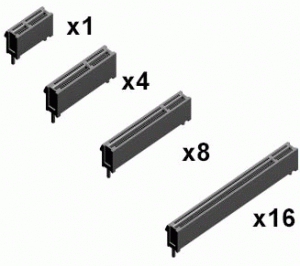
Modern video cards require a PCI Express (PCIe) slot to communicate with the system. Most video cards ask for a full-length PCIe slot with x16 or x8 bandwidth for an optimal operation.
Sometimes you can find video card that runs in the shortest expansion slot you can find on the motherboard, but they are usually entry-level video cards because this small slot can only have a x1 bandwidth.
Now in term of bandwidth, the x1 bus with Revision 2.0 can deliver up to 250 MB/s and this rate is multiplied by the bus type. For example : x8 can provide up to 4 GB/s while x16 tops at 8GB/s.
Revision 3.0 that has just come out recently doubles the x16 bus to roughly 15.8 GB/s.
All Revisions are always compatible to the next and previous generations, so you don’t have to worry whether PCIe 2.1 will work in a PCIe 2.0 or vice versa, etc… You just have to make sure the physical length of the video card PCIe interface match up with what you have in your computer.
On a useful note, most of today single-gpu video cards can do just fine in a x8 bandwidth by itself, without any major hit on the performance.
It only becomes important when you are running a multiple graphic cards setup such as SLI/Crossfire or a mutiple-gpu graphics card such GTX 690, Radeon 7990.
2. The Power Requirement
 The PCIe slot itself can deliver up to 150w to your device but in many cases you will need to provide additional power to the video cards.
The PCIe slot itself can deliver up to 150w to your device but in many cases you will need to provide additional power to the video cards.
Typically, a 500-watt power supply unit with more than 28-amp on the 12V+ rail should have no problem running a majority of video cards in the market.
We usually want to stay on the safe side and go after an expensive 800 or over 1000-watt PSU but it is totally unnecessary if there is only one GPU.
It is also very important to make sure how many 6-pin or 8-pin PCIe connectors the video card requires from the power supply unit so you will not run into the problem later on.
3. The Re-badged Product
 Graphics Processor manufacturers such as NVIDIA and Radeon always follows the periodically update pattern for their products due to peer pressure. They do this to compete against one another, in mean of being in the lead to provide the latest and newest technology to the hands of their beloved customers.
Graphics Processor manufacturers such as NVIDIA and Radeon always follows the periodically update pattern for their products due to peer pressure. They do this to compete against one another, in mean of being in the lead to provide the latest and newest technology to the hands of their beloved customers.
However, it is not always a good thing. For us at least.
When a new design or architecture comes out and it does not really matter whether that will be a better product than the previous generation or not, the manufacturers will rush this new hardware to the market under a totally new series or name.
Now this is really different to the central processor market. Upon the release of the new CPU, it is easy to distinguish the performance and break-through of the product.
In the graphics card market, you may find the new generation to your old video card performs (if not the same) just slightly better than the last year lineup; while it costs a lot more.
When you know which video card is the re-badged product of the previous generation, you will be able to eliminate a lot of doubts and misunderstandings due to the confusion in the graphics card market.
4. What Makes Performance ?
The key to be on top of all current video cards is also to have a general knowledge of each generation and their namesake.
For both AMD Radeon and NVIDIA families, you probably notice the higher the number in the same series usually means the better the performance. That also means the higher number in the name of the old series indicates that the video card is also faster than the lower number unit of the new series.
For instance, the NVIDIA GTX 550 Ti will be slower than NVIDIA GTX 560 since they are in the same family.
However, the late NVIDIA GTX 480 in the previous 400-series is actually much faster than the early batch GTX 520 in the 500-series.
EVGA GeForce GTX480 1536MB GDDR5 Dual DVI, HDMI, SLI Graphics Cards 015-P3-1480-KR
- GPU Core Clock : 700MHz
- GDDR5 Memory Clock: 3696MHz (Effective)
- CUDA Cores: 480
- PCI-E 2.0
EVGA GeForce GT 520 1024 MB DDR3 PCI Express 2.0 2DVI/Mini-HDMI Graphics Card, 01G-P3-1526-KR
- Microsoft DirectX 11 Support
- 1000 MHz Effective Memory Clock and 1620 MHz Shader Clock
- PCI Express 2.0
- GeForce GT 520 with 810 MHz core clock
In all cases, even though the performance is higher but the older architecture may consumes more energy and generates more heat. Yet, sometimes they are cheaper.
Another factor that usually misguides first-time video card buyers is the memory capacity.
It is often to get confused that the higher count of memory can justify the real speed and power. But that is not the only one cause. The amount of memory on mainstream gaming video cards plays a relatively small role and does not make a great impact on the performance, in most environment settings.
On the flip side, the type of memory does matter. On-board GDDR5 is a lot faster and more responsive than older DDR3.

You must also look in to the number of CUDA Processors (NVIDIA) or Stream Processors (Radeon) and know how fast the core clock speed is. These are the two significant elements that essentially determines the true in-game performance of the video card.
It is not advised to compare CUDA to Stream Processors because the way NIVIDIA and Radeon address their processor quantity are completely different to one another.
For example, the top of the line single-gpu NVIDIA GTX 680 has 1536 CUDA Processors and is in the same level as the Radeon HD 7970 who has 2048 Stream Processors.
However in some special case such as for bit-coin mining – all Radeons are much more better than NVIDIA counterparts.
On the other hand, NVIDIA is more efficient for graphics design or movie works due to its CUDA technology.
- When your current video card dies.
- When there is a new model that is at least TWICE as fast as your current mid-range video card and does not cost 40% more than the total amount you paid for the first one. If not, just be patience. Keep calm and wait for the best deal, not the expensive deal.
For example, when the Radeon HD 4850 first came out in 2008, it ran for nearly $200. Believe it or not, it still plays most of today games at a decent fps.
However if I have to upgrade to something noticeably better without having to sell my dog, that would be the Radeon HD 6870 (skipped a generation, the 5000 Series). It falls under $220 range in retail stores and less than $180 online.
Sapphire AMD Radeon HD 6850 1GB PCI-E Video Card (100315L)
- PCI-Express 2.0 x16 bus interface
- 256-bit DDR5 memory interface
- Microsoft DirectX 11 Support
- Microsoft Windows 7 Support, 1xHDMI, 1x Display port, 1xDVI
Another example is we should not give up a GeForce GTX 660 Ti for a GeForce GTX 770 because the cost does not justify the performance difference. Well you get the idea.
ASUS GTX 660 Ti Series Graphics Card Overclocked Edition Graphics Cards GTX660 TI-DC2O-2GD5
- TOP-selected 1058MHz core - 78MHz higher than reference for smoother gameplay.
- DirectCU thermal design utilizes direct contact copper heatpipes so heat is dissipated...
- GPU Tweak utility helps you modify and tune clock speeds, voltages, and fan performance...
- Acclaimed DIGI+ VRM with Super Alloy Power technology delivers precise digital power and...
MSI NVIDIA GeForce GTX 770 2GB 256-Bit GDDR5 DisplayPort DL-DVI-I, DL-DVI-D, HDMI, PCI Express 3.0 Graphics Card N770 TF 2GD5/OC
- Chipset: NVIDIA GeForce GTX 770
- Core Clock: 1137 MHz (OC Mode)
- Video Memory: 2GB GDDR5
- Memory Clock: 7010 MHz
- When your video card is more than 4-generation old to the latest in the market.
6. The Tips
- Fan Count does matter. Single fan video card tends to get noisy during heavy load and it isn’t as efficient as double fan design. Heat causes instant performance drop when you least expect.
- Special Editions such as Superclocked, OC, etc… are essentially the same chip as the regular model, but with better chip binning.
What is chip binning ? In short, it is the portion toward the center of the silicon wafer that can produce extremely power efficient, more powerful and higher quality chips than the outer areas.
As for a CPU example, we would compare the mainstream processors to the Xeon processors.
When it comes to GPUs, it is usually the normal generic video card versus the super-clocked edition, such as GeForce GTX 570, GeForce GTX 570 FTW, etc..
Step 2 »
Shopping Day : Choosing the Right Video Card for Your Computer








Geeze, has this writer never heard of proof-reading? How tacky and noobish.